The MIPSA Student Research Club at the Institute of Electronics at the Lodz University of Technology is looking for new members! 💡 If you are interested in electronics, telecommunications, radar systems, satellites, programming or data analysis, this is the place for you.
Authored on
Kategorie
Institute of Electronics is participating in the research project "Deep Learning – Based Highly Precise Detection of Weeds and Development of Robust and Precision Weeding Technologies", led by Jeonbuk National University, Republic of Korea. 🇰🇷
Authored on
Kategorie
From September 10–12, 2025, the Radiocommunication and Teleinformatics Conference (KRiT) took place in Gdańsk – a nationwide forum bringing together researchers and representatives of the IT industry. The conference focused on the latest trends in radiocommunication and teleinformatics, including next-generation networks and systems, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and cloud technologies. 🌐🤖🔐
Authored on
Kategorie
Graduates of the Biomedical Engineering program, Lena Cieślak and Emilia Stodulska, presented the results of their engineering theses at the 28th Conference SPA 2025 - Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and Applications in Poznań. ✨
Authored on
Kategorie
We are pleased to announce that three students of the Biomedical Engineering program from the Institute of Electronics at Lodz University of Technology took part in the prestigious NBC 2025 & PCBBE 2025 conference in Warsaw 👉 https://nbc2025.ibib.waw.pl/ 🌍💬
Authored on
Kategorie
Lena Cieślak and Emilia Stodulska, students of the Biomedical Engineering program, presented the results of their engineering projects yesterday at the nationwide SECON 2025 conference in Warsaw.
Authored on
Kategorie
Medical Electronics Division - niezastąpiona w diagnostyce, leczeniu i rehabilitacji
Authored on
Kategorie
Elevated temperature is the dominant cause of electronic systems failures, accounting for 55% of them. Thus, there is a need for thermal characterization of electronic circuits. One of main methods of describing their thermal properties is the thermal impedance approach. The mathematical foundations for such measurements were laid down in the JEDEC JESD51 standards series. A system for thermal impedance measurements using a fast, single detector IR sensor was designed and tested, along with dedicated software for thermal characterization of electronic circuits, based on upper surface temperature measurement.
Authored on
Kategorie
Explosive and poisoned gases leakage causes the danger for people both in industry and at home. The example is the methane in coal mines. The imaging systems presenting the distribution of gas concentration from a distance is the alternative for widely-used single detector sensors. Moreover, due to the warming effect, climate changes and environment protection, there is a growing interest of using remote gas imaging systems. We do both the research and developments in this field. As the example, the high-sensitive bolometer cameras we have successfully used for detection methane, ammonia and carbon dioxide (CH4, NH3, and CO2).
Authored on
Kategorie
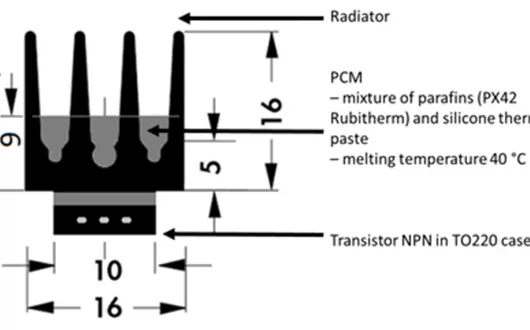
Thermal management is one of the most important issues for electronic devices producers. The market of electronic devices grows very fast as well as power densities dissipated in electronic components. Dimensions of the devices and their packages are getting smaller. Electronic devices are operating well in specified range of temperature. Overheating of electronic elements leads to their shorter lifetime, malfunction (e.g. logic errors in microprocessors) or even immediate breakdown. As the result of above pointed facts, there is a need to design and produce advanced cooling systems that would fulfil the thermal management requirements in a superior way.