Worldwide, there are 314 million of visually impaired and 45 million of them are blind. According to EU reports for every 1000 Europeans 4 are blind or visually impaired. Vision loss is the most serious sensory disability that causes approx. 90% depravation of entire multi sense perception for a human. In spite of a long lasting research efforts independent mobility and orientation aids for the blind still await for a ground-breaking technology that would effectively support visually impaired. No single solution of electronic travel aids has gained a wider acceptance within the blind community. The white cane (with no mounted electronics) still remains the primary travel aid for the blind [1].
Human-computer interaction
Authored on
Kategorie
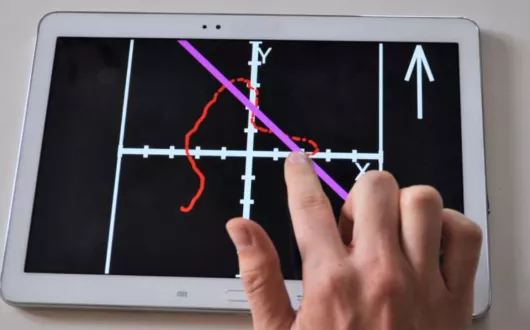
One of the main barriers encountered by blind people is access to graphic information, including photos, maps, drawings and pictures. There is a need to develop effective methods for processing visual information into sensory signals that are accessible to blind people. This work concentrates on expanding and acquiring new knowledge in the field of presentation of visual scenes for the blind using the senses of touch and hearing. The research hypothesis is as follows: it is possible to develop tactile-controlled sound patterns allowing the blind user to correctly interpret the image displayed on the touch screen.
Authored on
Kategorie
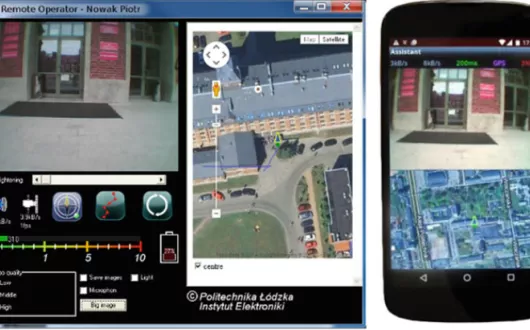
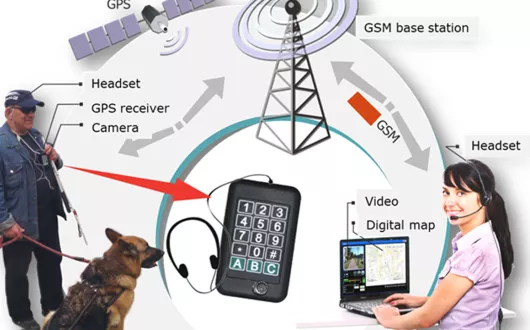
Even the best electronic travel aids (ETAs) supporting blind people in independent travel are unable to provide assistance that another person can offer. Modern cell phones are equipped with very efficient processors and, often, very good quality digital cameras. Almost every smartphone is equipped with a set of position sensors enabling the detection of phone movement, its GPS location and orientation. Data recorded by mobile phones can be used as additional information needed to obtain support for a blind person from a remote assistant equipped with a suitable terminal.
Authored on
Kategorie
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) are devices, which acquire raw brain activity signals, analyze them, and translate them into commands that are transferred to output devices. In such a way BCI communication systems are independent from the brains regular output pathways of peripheral nerves and muscles. For that unique reason, such devices may someday enable people with disabilities, including paralyzed people to use the computer and other technical equipment, on a par with other users.
Authored on
Kategorie
In the era of the information society, the computer has become an indispensable personal tool used in in fact in every area of life. Information and communication technologies (ICT) should be available to all potential users, regardless of their age, disability or type of equipment used. Therefore, it is necessary to design these tools according to the principles of universal design for ICT and recommendations described in three documents prepared by the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium): Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines (ATAG) and User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG).