Development of numerical methods for modelling and estimation of kidney perfusion using magnetic resonance imaging
The aim of the project is to develop improved methods for estimating renal perfusion parameters from magnetic resonance images and tools for their objective, quantitative validation.
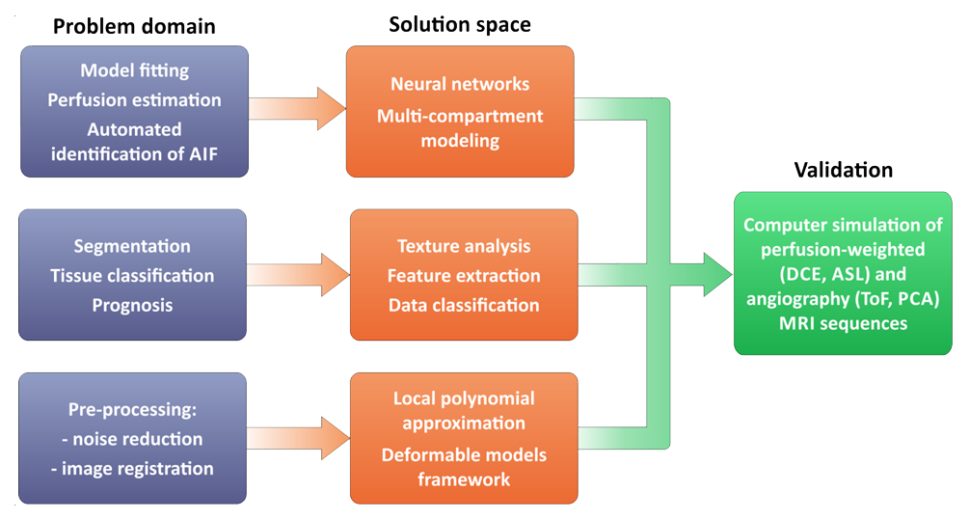
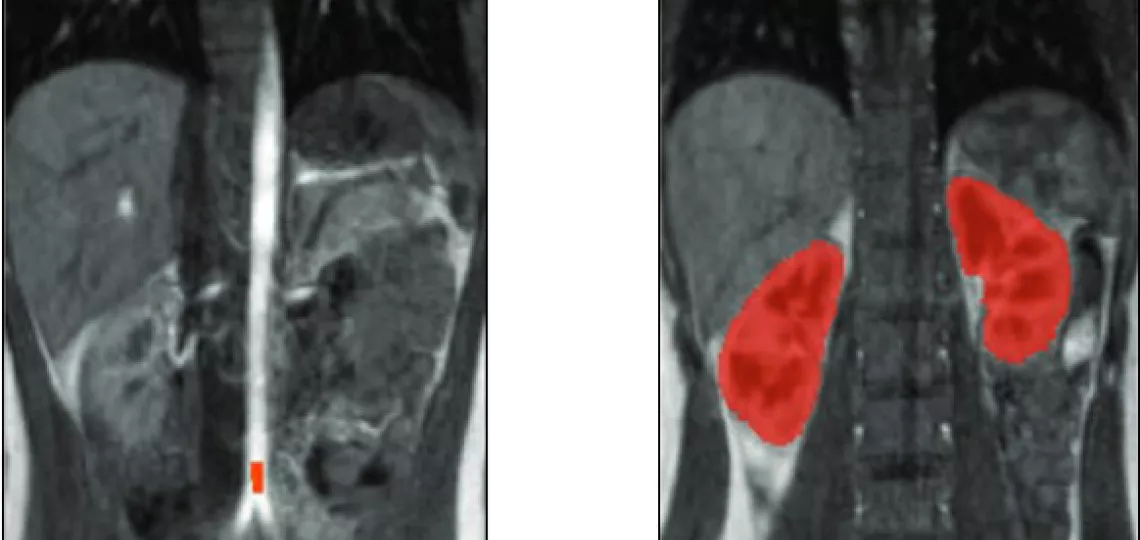
The subject of the project's research is the perfusion of the kidney - one of the body's most vital organs due to its key role in regulating a variety of bodily functions. One of the methods available to assess renal function is the visualisation and estimation of renal perfusion using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. An analysis of the current state of the art in perfusion-dependent MR image processing reveals a lack of a standardised methodology for determining its parameters. A number of pharmacokinetic models of renal perfusion are defined, but the results of calculations based on these often lead to quite different assessments of renal perfusion capacity. The proposed solutions are preliminary and partial. Hence, the aim of the project is to develop improved methods for estimating renal perfusion parameters from magnetic resonance images and tools for their objective, quantitative validation. It is assumed that a magnetic resonance imaging simulator for perfusion-dependent sequences (such as DCE-MRI and ASL), created for validation purposes, will allow the limits of applicability and accuracy of measurements based on the developed methods to be determined.
The research hypothesis refers to specific image processing methods that have been shown to be effective in previous work by the authors, but whose use in the context of perfusion imaging has not yet been reported. Namely, it is planned to prove that a combination of texture analysis methods, machine learning, deformable models and local polynomial approximation will allow more accurate, reliable and reproducible estimates of perfusion parameters from magnetic resonance images.
Project leader: dr inż. A. J. Klepaczko
Years: 2015 – 2019
Project type: NCN-OG, NCN ST7 / OPUS-8 Grant; fundamental research
Key publications resulting from the project:
- Klepaczko Artur, Szczypinski Piotr, Strzelecki Michał, Stefanczyk Ludomir: Simulation of phase contrast angiography for renal arterial models. BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING ONLINE, 2018, vol. 17, nr 41.
- Klepaczko Artur, Szczypinski Piotr, Eikefjord Eli, Rorvik J., Lundervold Arvid: Estimating glomerular filtration rate of the kidney based on texture analysis of DCE-MRI images. MAGNETIC RESONANCE MATERIALS IN PHYSICS BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE, 2017, rocznik 30, nr 1, s. 388-389.
- Klepaczko Artur, Szczypinski Piotr, Strzelecki Michał, Stefanczyk Ludomir: Towards simulation of 3D Phase Contrast imaging of kidney vasculatures. MAGNETIC RESONANCE MATERIALS IN PHYSICS BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE, 2017, rocznik 30, nr 1, s. 521-522.
- Klepaczko Artur, Szczypinski Piotr, Deistung Andreas, Reichenbach J., Materka Andrzej: Simulation of MR angiography imaging for validation of cerebral arteries segmentation algorithms. COMPUTER METHODS AND PROGRAMS IN BIOMEDICINE, 2016, rocznik 137.