Radio monitoring system for firefighter activity and physiological status
Łukasz Januszkiewicz, Sławomir Hausman, Tomasz Kacprzak
Due to developments in technology and the miniaturisation of integrated circuits, radio communications can be used in an increasing number of mobile electronic devices. The benefits of wireless connectivity make it expedient to use it also in textronic devices. This creates the need to embed radio path components directly into clothing. For this purpose, it is necessary to develop both new methods for designing such elements and technologies for their manufacture.
The designed textile antenna contains, like the V antenna, a radiator composed of two arms, the converging ends of which are connected via a two-wire power line with a symmetriser and a power cable.
Unlike the original design, the radiator arms are curved according to the shape of the exponential function and are made of conductive yarn attached to a top and base layer made of textile material.
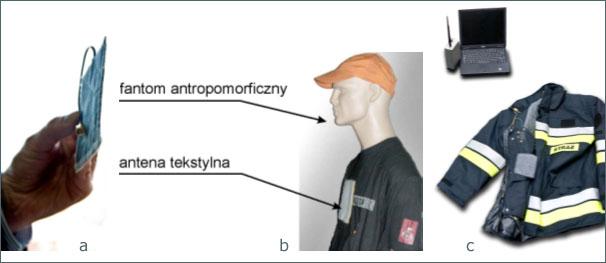
Measurements of the radiation characteristics of the antenna were carried out on an open test ground with a conductive reference ground. Due to the intended use of the designed antenna for installation in clothing, the antenna under test was placed on a phantom imitating the human body.
The antenna's parameters allow it to be used in textronic systems using radio communication in the commonly used unlicensed band 2.4 ÷ 2.5 GHz. Due to its small size, weight and volume, as well as high flexibility, the antenna can be successfully placed inside clothing, as it does not limit the freedom of human movement, does not cause discomfort and ensures high performance of clothing, e.g. the possibility of easy maintenance.
The parameters of the presented antenna are influenced by the location in relation to the human body and the deformation. In further research, the antenna prototype will be used to investigate changes in antenna parameters for different locations relative to the body.
Gold medal Brussels-Eureka! 2009